NMPF’s chief veterinary officer Meggan Hain explains for listeners of Dairy Radio Now how the FARM program’s Animal Care component is in the process of implementing the latest set of industry care standards, and how NMPF is organizing outreach and education sessions across the producer community to help facilitate the uptake of the program.
Tag: dairy industry
Whole Milk for Healthy Kids: Now is the Time
After years of patient effort, Congress seems headed for a long-overdue correction to misguided nutrition policy. The Whole Milk for Healthy Kids Act is moving forward, and with it an opportunity to better nourish the next generation of American schoolkids.
We’ve been down this road before. The same legislation passed the House of Representatives with overwhelming bipartisan support in 2023, but the Senate didn’t consider it before time expired in that Congress. This time, Senate prospects are stronger. Last month, the Senate Agriculture Committee reviewed the bill at a legislative hearing, which showcased the strong bipartisan support the measure enjoys. Its House counterpart committee has already approved it, and we are hopeful for similar Senate action.
After that, the next step is the floor. With overwhelming bipartisan support in both chambers, this legislation is a chance for both parties to agree on something – and that’s too good of an opportunity for Congress to pass up. More likely, lawmakers will want to move quickly, showing their constituents a win on a popular – and important – issue.
From a nutrition standpoint, bringing whole and 2% milk back into schools, which the legislation would allow, is a no-brainer: Kids benefit from consuming high-quality nutrition, and whole milk is a high-quality nutritious food they will actually consume. This is even more important, considering that roughly 90 percent of the U.S. population does not meet current dairy recommendations, as USDA recently told the Senate Ag Committee.
School meals rules in effect since 2012 only allow 1% and fat-free milk options, ostensibly to reduce calorie intake and combat childhood obesity. That oversimplifies the complexities of child nutrition. Whole milk is a rich source of essential nutrients such as calcium, vitamin D, and potassium, all of which are crucial for the development of strong bones, teeth, and muscles. The fats present in whole milk also play a vital role in brain development and overall growth. Most importantly, kids prefer whole milk. That boosts consumption and reduces food waste. Better used, better-targeted nutrition is a compelling combination the Whole Milk for Healthy Kids Act would achieve.
Putting whole milk in schools also aligns with the latest dietary science. The demonization of dietary fats, particularly saturated fats found in whole milk, is being increasingly debunked – but the widespread misconceptions they have fostered take time to turn around. Emerging research suggests that saturated fats are not inherently detrimental when consumed as part of a balanced diet; in fact, they help absorb fat-soluble vitamins and provide long-lasting energy that is essential for active children. By excluding whole milk from school menus, we may be depriving children of these critical benefits.
We’re also depriving them of what parents overwhelmingly choose to serve them at home. In 2012, the year changes to school meals guidelines eliminated whole milk as an option, 69 percent of fluid milk bought at retail was whole or 2% milk. After a dozen years of kids being forced to consume only skim or 1%, that percentage rose to 81 percent. It’s time to stop swimming against the tide and align schools with parental choice.
Ultimately, the Whole Milk for Healthy Kids Act is about making informed, science-backed decisions that prioritize the health and future of our children. We’ve been active boosters of this legislation, sponsored in the House by Rep. Glenn ‘GT’ Thompson, R-PA, and Rep. Kim Schrier, D-WA, and in the Senate by Sen. Roger Marshall, R-KS, and Sen. Peter Welch, D-VT, every step of the way. As it moves forward, expect us to be asking for your support. (You can subscribe to our Advocacy Alerts, along with other NMPF publications, here.) This legislation is a meaningful step towards ensuring that every child has access to the essential nutrients they need to thrive. It isn’t an opportunity we want to miss.
The Whole Milk for Healthy Kids Act is not just a legislative proposal; it’s a path toward a healthier, more nutritionally sound future for our children. It’s vital that Congress moves swiftly to enact it into law. Our children’s health and well-being depend on it.
Gregg Doud
President & CEO, NMPF
NMPF’s Bjerga on Dairy, the Snacker’s Choice
Recent data is showing that even as snack food consumption stagnates, dairy-focused products such as Greek yogurt and cottage cheese are increasing sales volumes. NMPF Executive Vice President Alan Bjerga breaks down why in an interview with RFD-TV.
Regulatory Register – Winter 2025
NMPF’s Bleiberg Offers Update on House Legislation to Increase School Milk Choices
NMPF’s executive vice president Paul Bleiberg tells the listeners of Dairy Radio Now about the passage this week by the House Education and Workforce Committee of new legislation that would increase the range of milk options available to school children. The Whole Milk for Healthy Kids Act would give schools the option of serving 2% and whole milk once again. The bill is now expected to move to the full House for further consideration.
NMPF’s Bjerga on Whole Milk, Lactose-Free Gains
Consumers are increasingly turning to whole milk, an important point to consider as Congress considers the Whole Milk for Healthy Kids Act, NMPF Executive Vice President Alan Bjerga says in an interview with Big Radio in Janesville, WI. Along with whole milk, consumers are also drinking more lactose-free varieties, an important part of the industry’s future.
NMPF’s Bleiberg Reviews Capitol Hill Agenda in New Year
NMPF’s executive vice president Paul Bleiberg discusses the current agenda for Congress as the leadership transitions in Washington from President Biden to President-elect Trump. Bleiberg also highlights that the USDA plans to soon open the 2025 sign-up for the Dairy Margin Coverage program, for those farmers not already enrolled in the federal safety net.
NMPF’s Bleiberg Assesses Agenda for Congressional Lame Duck Session
NMPF’s chief lobbyist Paul Bleiberg explains for listeners of Dairy Radio Now what Congress will focus on during the first few weeks of December in the congressional lame duck session that is following last month’s election. Members of the House and Senate will have to address government spending for 2025, but are not expected to pass a new farm bill in 2024, instead preferring to extend current policy and work on a new version next year.
NMPF’s Bjerga Discusses Rising Dairy Consumption
https://www.rfdtv.com/keep-it-flowing-u-s-per-capita-dairy-consumption-returns-to-1950s-levels
NMPF Executive Vice President for Communications & Industry Relations Alan Bjerga discusses new USDA data showing that per-capita dairy consumption among Americans is back to 1950s levels, in an interview with RFD-TV. Robust holiday sales could push consumption to even higher levels. “We can do this, America,” Bjerga said.
NMPF’s Bleiberg Analyzes November Election Results
NMPF’s chief lobbyist Paul Bleiberg assesses for listeners of Dairy Radio Now how the election of former president Donald Trump, along with a Senate majority led by the GOP, will impact dairy policy and agricultural issues in Washington and in farm country going forward.
Dairy Diversity Ready to Grow
It might sound crazy to think that a product that’s already in 94 percent of U.S. households has room to grow, but the numbers indicate it’s true. Here’s what we’re talking about:
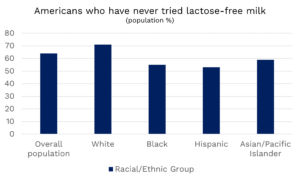
This comes from a study done by the International Food Information Council, supported by NMPF and the International Dairy Foods Association, on consumption habits among diverse U.S. populations. What’s striking is that, even though self-reported lactose intolerance among non-White populations runs at roughly 30 percent (according to the same study), clear majorities among Black, Hispanic and Asian/Pacific Islander populations haven’t even tried milk that addresses that intolerance, forgoing an option that provides 13 essential nutrients. And presumably, some of those non-milk drinkers are in that 6 percent who don’t have it in their refrigerators.
(And conversely, some of that 94 percent must include lactose-intolerant consumers. Are they taking lactase pills to aid in digestion? Are other household members the milk drinkers? There’s still much to know.)
The point is this: At a time when the committee drafting recommendations for the next Dietary Guidelines for Americans is looking at nutrition science and contemplating recommendations that are appropriate to the lived experiences of a wide range of Americans, it’s important to meet people where they are. For the overwhelming majority of them, that means a place where they have milk in the fridge. Those who aren’t there are in a place where awareness of the numerous ways to benefit from dairy nutrition, regardless of lactose tolerance, isn’t what it needs to be.
That suggests a need to double down on offering dairy’s benefits in a way that’s tailored to the needs of individual communities. It means listening to communities that value dairy and wish it could be offered more readily, in more accessible forms. It means serving that 94 percent of households with milk — and using the tools available to raise that percentage. It emphatically does not mean de-emphasizing dairy as a critical nutritional option for all Americans — or even worse, suggesting it be replaced by sources that aren’t nutritionally equivalent.
NMPF has a call to action that dairy advocates can use to help get this message across. Public health, and the best public health guidance, is important to all Americans. And dairy is ready to provide high-quality nutrition that’s affordable and accessible to all.
U.S. defends dairy in Colombia
 By Jaime Castaneda, Executive Vice President, National Milk Producers Federation
By Jaime Castaneda, Executive Vice President, National Milk Producers Federation
NMPF and the U.S. Dairy Export Council (USDEC) are working to preserve market access for American dairy exports to Colombia following the Colombian government’s abrupt July 5 decision to initiate a politically driven “subsidies and countervailing measures” investigation into milk powder imports form the United States.
The move has little to do with U.S. milk and everything to do with Colombia’s domestic politics. In an effort to reverse slipping popularity with voters, the Colombian government has decided to misuse trade tools usually reserved for private industry to counter legitimate damage from “dumped” product sold at below market rates. In contrast to this, Colombia’s government has instead launched this case on its own, alleging that U.S. milk powder exports from 2020 to 2023 were unduly subsidized by U.S. government programs and damaged Colombian dairy producers. Unfortunately, due to the investigation’s political nature, the Colombian government could impose tariffs on imported U.S. milk powder products as early as September 16. That would be certain to stifle trade to the market.
NMPF and USDEC have been working with U.S. exporting cooperatives and companies, legal teams, and the U.S. government to submit a strong, data-driven defense proving that this investigation is without merit.
In their counterarguments, NMPF and USDEC note that the investigation is baseless for many reasons, including:
- Product comparison: Imported U.S. milk powder and domestically produced Colombian fluid milk are distinct products with different physical characteristics and end uses, making them non-comparable.
- Subsidy misinterpretation: The Colombian government incorrectly assumes that U.S. dairy producer support directly benefits milk powder manufacturers, which is not the case.
- Lack of causal link: U.S. milk powder imports haven’t caused any damage to the Colombian dairy industry. Evidence simply doesn’t exist.
Because of the political nature of this investigation, a fair result is not guaranteed, which means that U.S. government intervention may be necessary. NMPF and USDEC are urging U.S. Trade Representative Katherine Tai and U.S. Department of Agriculture Secretary Tom Vilsack to use all available tools to respond forcefully should Colombia impose tariffs on U.S. milk powder imports despite the lack of evidence meriting such a result.
Congress is also paying attention. A letter sent by the bipartisan leads of the U.S. House of Representative’s Agricultural Trade Caucus to the Colombian Ambassador to the United States highlights the U.S. dairy industry’s long-standing commitment to work with its Colombian counterparts and encouraged the two industries to work together to strengthen the dairy sectors in both countries instead of pursuing meritless investigations.
Colombia’s investigation will play out over months, starting with preliminary results and potential provisional measures as early as September 16, followed by a public hearing and additional comment periods.
At stake is $70 million in annual U.S. milk powder exports to Colombia.
While not a trivial amount by any means, this investigation could also set a dangerous precedent for like-minded governments to imitate. Over the past several years, protectionist sentiments have grown around the world, and Latin America is no exception. The region has become a battleground in the effort to preserve existing trade opportunities, flaring up from Peru and Ecuador to Brazil and Mexico.
While cooperating with the investigation, NMPF and USDEC continue to engage with policymakers and allied organizations to seek a positive conclusion. Regardless of which way this investigation turns out, it’s important for the United States to respond forcefully and let its trading partners know that such maneuvers will not be tolerated.
This column originally appeared in Hoard’s Dairyman Intel on Sept. 5, 2024.






