The federal government is pressing ahead in crafting a new iteration of the Dietary Guidelines for Americans, the twice-a-decade guide to science-based advice on what to eat and drink for health and well-being. The guidelines also inform federal nutrition programs, such as school meals and food assistance.
Dairy, to no one’s surprise, is critical to the discussion. For the sake of our nation’s health, this discussion has to be done right, with proper deliberation and dairy maintaining its role as a central component of healthy eating.
A committee of experts is reviewing the latest evidence and preparing recommendations for the next iteration of the guidelines, due next year. As we said in the comments we submitted to that committee: Dairy foods are essential for optimal nutrition and health. Foods such as milk, cheese and yogurt provide a unique package of nutrients American often lack, such as calcium, vitamin D, potassium, protein and iodine. Dairy also reduces chronic disease risk, lowers blood pressure, improves blood sugar control, and protects bone health. And dairy is especially important for children, who need adequate calcium and protein for growth and development.
When the government released its current guidelines in 2020, it noted that dairy is under-consumed by 89 percent of the population. Dairy’s role as a critical nutrient provider, and its underconsumption, is why dairy needs to continue as its own food group, with three recommended servings per day, in the 2025 guidelines. That standard is consistent with current practice, reflected in the nutrition guidance of many other countries and health organizations, and supported by decades of scientific research. Guidelines that don’t give dairy its due simply would not be credible – not when the science, the general public and the mainstream nutrition community all recognize that, without dairy, health outcomes suffer and families, especially families with children, don’t get the nourishment they need.
Maintaining dairy’s place at the bedrock of proper nutrition is of paramount importance as the guidelines are under review. NMPF is fighting for dairy’s necessary pride of place through our public comments, our meetings at all levels of decision-making, our partnerships with allied organizations, and our daily fight against anti-dairy misinformation in media interviews and outreach. Because, as is inevitable in Washington, the guidelines are the subject of intense advocacy efforts, often by groups that have goals in mind other than better nutrition.
For example, some vegan and environmental activists are pushing for replacing some dairy foods with plant-based alternatives in the guidelines, all in the name of reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Even setting aside the flawed sustainability arguments, the answer to that is no. Plant-based products are not nutritionally equivalent to dairy foods and do not have the same health effects. In fact, most plant-based alternatives are low in protein and have added sugars, oils, and synthetic nutrients that are in no way nutritionally equivalent to dairy in terms of human health.
Children who consume plant-based alternatives instead of dairy may be at risk of nutritional deficiencies, growth impairment, and bone fractures. Pregnant women who avoid dairy may not get enough iodine, which is essential for fetal brain development. Three of the four nutrients identified in 2020 as issues of public concern because of their widespread under-consumption — specifically vitamin D, calcium and potassium — are abundant in dairy, but not so much in plant-based products. And low-income consumers who choose plant-based alternatives may face higher food costs and lower nutrient density.
And when we talk about low-income consumers, inevitably we need to talk about equity. Dairy foods are widely available, affordable, and culturally acceptable for most Americans. They’re also a major component of federal nutrition programs, such as school meals and WIC, which serve millions of low-income and vulnerable Americans and help ensure that children and families have access to nutritious foods that support their health and learning.
Dairy is an excellent nutritional option for populations who face disproportionate rates of chronic diseases, such as hypertension, diabetes, and osteoporosis. And dairy foods can accommodate different preferences and needs, such as lactose intolerance, vegetarianism, or environmental concerns.
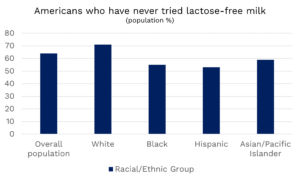
Contrary to the claims of misguided social-justice activists that dairy products can’t possibly serve diverse populations because of intolerance, the reality is that lactose-free and low-lactose dairy products, such as lactose-free milk, yogurt, and hard cheeses, can provide the same nutrients and benefits as regular dairy. For all these reasons and more, dairy needs to maintain its prominence in American diets, in federal programs, and in the Dietary Guidelines for Americans.
The guidelines also need to be the product of thoughtful, science-based, and careful deliberations. Another threat facing dairy is that, as election-year politics combine with activist agendas, a devil’s brew of flawed science and ill intentions could result in hastily released guidelines that do a disservice to American health and destroy the very legitimacy of the guidelines. This is the worst possible outcome of all – and it’s one we’re guarding against as we work on this issue through the fall.
Dairy foods are essential for optimal nutrition and health. They provide a unique package of nutrients, they’re an equitable option for health and wellness, and they’re widely available, affordable, and culturally acceptable for most Americans. They deserve thoughtful consideration and a prominent place in the dietary guidelines, as well as in our plates and cups.

Gregg Doud
President & CEO, NMPF

 By Miquela Hanselman, Director of Regulatory Affairs, National Milk Producers Federation
By Miquela Hanselman, Director of Regulatory Affairs, National Milk Producers Federation