NMPF Poised for Action-Packed 2025 as Republicans Sweep
December 04, 2024NMPF is analyzing the results of the 2024 elections, building new relationships and strengthening old ones as business-as-usual in Washington promises to shift next year with Republican control of the White House and both houses of Congress.
In preparation for this “trifecta” next year, House and Senate Republicans elected their leadership teams immediately following the November elections. House Republicans voted to keep in place Speaker Mike Johnson, R-LA, Majority Leader Steve Scalise, R-LA, and Majority Whip Tom Emmer, R-MN, while electing Representative Lisa McClain, R-MI, as Republican Conference Chair.
Representatives Emmer and McClain both represent sizable dairy footprints. In the Senate, Republicans elected Senator John Thune, R-SD, a longtime dairy ally and Senate Agriculture Committee member, to serve as their Majority Leader next year. Sens. John Barrasso, R-WY, Tom Cotton, R-AR, and Shelley Moore Capito, R-WV, were elected to the other top leadership spots of Majority Whip, Republican Conference Chair, and Republican Policy Committee Chair, respectively.
House Republicans in December are likely to work with President Biden and Senate Democrats to extend several expiring laws on a short-term basis so that they can tackle them next year with complete control of the nation’s capital. Congress also is on track to pass another one-year extension of the 2018 farm bill before adjourning.
This year’s House farm bill and Senate frameworks included numerous dairy priorities, such as requiring USDA to conduct mandatory manufacturing cost surveys every two years, prioritizing the protection of common food names in trade discussions, and allowing schools to serve nutrient dense whole milk. Should a new farm bill not be passed this month, NMPF will once again advocate for a new farm bill next year that meets dairy’s needs. However, an extension at least would ensure that the Dairy Margin Coverage program continues without disruption.
Congress also is likely to extend government funding on a short-term basis, possibly until March. The House and Senate 2025 agriculture funding bills included several NMPF-backed provisions, including House language to reverse the reduction in the maximum monthly milk allotment in USDA’s final foods package rule for the Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children and Senate language mirroring the Innovative FEED Act to allow the Food and Drug Administration to review animal feed additives in a more efficient manner.
While a short-term funding extension will require the new Congress to complete the full-year 2025 bills, the bills drafted this year will likely serve as the starting point for final negotiations next year.
The 119th Congress that convenes in January will have a full plate that extends well beyond finishing this year’s business. An extension of the debt limit, the federal government’s borrowing authority, will come due in the first quarter of the year. Then, with full control of Washington, Republicans are expected to turn their attention to extending the expiring provisions of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017, one of President-elect Trump’s signature accomplishments from his first term.
NMPF will urge Congress to continue several pieces of the 2017 law, including the Section 199A domestic manufacturing tax deduction that allows agricultural cooperatives to pass the proceeds directly back to their farmer-owners. Congress is likely to complete this process using the tool known as budget reconciliation, which allows for the consideration of certain taxation and spending legislation not subject to the Senate’s 60-vote filibuster requirement.
H5N1 Response Evolves with FDA, USDA Studies
December 04, 2024NMPF staff is providing key input into federal mitigation efforts and leading dairy-farmer response as the H5N1 situation evolves. NMPF has participated in federal-led planning groups that have been meeting daily for months, and the NCIMS Executive Board is heavily engaged with those planning groups, as well.
FDA is in the final week of its milk silo testing study, which began Oct. 28. Through the six-week study, FDA has collected samples from raw milk storage silos at dairy processing facilities in participating states. This voluntary, double-blinded study is designed for data-gathering purposes only, with no way to trace back to individual farms. In the first three weeks of FDA’s study, only one sample tested positive for H5N1.
USDA hopes to begin its monitoring effort after FDA’s study concludes. The USDA monitoring effort is different from FDA’s and will be ongoing. Under USDA’s monitoring effort, samples will be taken from each raw milk silo at processing locations on a periodic basis. When a silo is determined to be positive, state animal health officials will be notified who will in turn assist farms associated with the positive sample.
Several states have implemented their own programs with mandatory bulk testing of milk to reduce the spread of H5N1, including California, Colorado, Michigan, Oklahoma, and Pennsylvania. These individual state testing programs are separate from the testing conducted by FDA and the upcoming USDA testing program.
The Pennsylvania Department of Agriculture announced Nov. 20 that it would begin mandatory testing of milk from Pennsylvania dairy farms. Though no cases of H5N1 have been detected in Pennsylvania cattle, the commonwealth is implementing this program to help with early detection.
Any cooperative or milk processor marketing milk from a Pennsylvania dairy farm must collect samples of raw milk taken from each compartment of each milk tanker from every pickup route once every 14 days to ensure that all farms supplying milk to those plants are covered. Samples must be taken by trained, certified personnel and submitted to a Pennsylvania Animal Diagnostic Laboratory System lab within 48 hours of collection. All testing will be handled with no out-of-pocket cost to the farmer, milk processor, or hauler. If milk from a tanker truck tests positive for H5N1, the Pennsylvania Department of Agriculture will work with the processor to determine which farms supplied milk to that tanker. From there, the Bureau of Animal Health will take samples from individual farms to determine the source and work with those farmers on biosecurity measures to prevent further spread. More about the PA program can be found here.
October DMC Margin Recedes $0.40/cwt from September Record
December 04, 2024The monthly margin under the Dairy Margin Coverage (DMC) program decreased by $0.40/cwt from September’s record level to $15.17/cwt. The October all-milk price was down $0.30/cwt from September to $25.20/cwt, while the DMC feed cost formula rose again from September, by $0.10/cwt of milk, mostly on a higher price for premium alfalfa hay.
The end of November dairy and grain futures indicated the DMC margin would average around $11.85/cwt for all of 2024.
Record DMC margins and relatively high prices come as policy and market developments continue to keep the NMPF/U.S. Dairy Export Council Joint Economics team busy with market analysis and events
NMPF Senior Director for Economic Research & Analysis Stephen Cain presented a market outlook to the ADPI Risk Management Seminar on Nov. 6 in Chicago and an FMMO and a farm bill update to Texas Farm Bureau virtually on Nov. 7. Will Loux gave an overview of the impact of H5N1 on the market to the Innovation Center Animal Care Committee virtually on Nov. 14.
FARM Showcases Sustainability Progress
December 04, 2024The National Dairy Farmers Assuring Responsible Management (FARM) Program highlighted the launch of FARM Environmental Stewardship Version 3 at the Fall Meeting of the Dairy Sustainability Alliance, highlighting progress in dairy sustainability and stewardship.
Nicole Ayache, NMPF’s chief sustainability officer, took the main stage to talk about the recent kick off and its incorporation of the Ruminant Farm System (RuFaS) model, a whole-farm model that simulates dairy farm production and environmental impact. Vermont dairy farmer Brian McGarry joined Ayache, sharing insights and opportunities for farmers and their cooperatives to evaluate potential technologies and measure progress.
FARM’s Senior Director of Animal Care, Beverly Hampton Phifer, led animal care evaluators through Version 5 training in Green Bay, WI. Evaluators must be re-certified every updated version cycle and attend a recalibration training annually. This marks the ninth training of the year, with the last training for 2024 taking place last Monday in Fresno, CA.
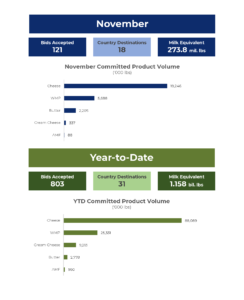
November CWT-Assisted Export Sales Nearly 27.6 Million Pounds
December 04, 2024CWT member cooperatives secured 121 contracts in November, adding 27.6 million pounds of product to CWT-assisted sales in 2024. This is equal to 273.8 million pounds of milk in milk equivalent on a milkfat basis. These products will go to customers in Asia, Oceania, Middle East-North Africa, Central America, the Caribbean and South America and will be shipped from November 2024 through May 2025.
Exporting dairy products is critical to the viability of dairy farmers and their cooperatives across the country. Whether or not a cooperative is actively engaged in exporting cheese, butter, anhydrous milkfat, cream cheese, or whole milk powder, moving products into world markets is essential. CWT provides a means to move domestic dairy products to overseas markets by helping to overcome U.S. dairy’s trade disadvantages.
The amounts of dairy products and related milk volumes reflect current contracts for delivery, not completed export volumes. CWT will pay export assistance to the bidders only when export and delivery of the product is verified by the submission of the required documentation.
NMPF Builds on Strong China Relationship
December 04, 2024NMPF Executive Vice President for Policy Development & Strategy Jaime Castaneda traveled to Shanghai and Beijing the week of Nov. 4 as part of NMPF and the U.S. Dairy Export Council’s ongoing efforts to grow U.S. dairy’s market share in China.
Joined by USDEC President and CEO Krysta Harden, Castaneda presented at the China International Import Expo and the Global Dairy Conference, highlighting the U.S. dairy’s commitment to being a reliable supplier of high-quality, safe, and sustainable products.
While in China, Castaneda and Harden delivered a new proposal to lower China’s most favored nation tariffs for cheese to Madam Yu, the Vice President of the China Chamber of Commerce of Foodstuffs and Native Produce. Like U.S. dairy’s successful tariff reduction effort in 2017, the proposal would improve market access for U.S. dairy producers to the top dairy importing country in the world.
The trip to China is just the latest NMPF and USDEC effort to grow the dairy relationship between the two countries. Castaneda in September spoke at a U.S-China Bilateral Agriculture Industry Roundtable on the opportunities for American ag companies in China. That came on the heels of a USDEC-USDA Foreign Agricultural Service business development mission to Beijing and Shanghai in June, which helped to fortify relationships between U.S. dairy suppliers and Chinese buyers and strengthen ties with Chinese trade associations and government agencies.






